
In April we had the opportunity to present our „SuMatHrA“ light wood project at the booth of the Federal Ministry for Economic Affairs and Climate Action (BMWK) at the Hannover fair.
„SuMatHrA“ stands for “Substitution of conventional materials for lightweight construction with wood hybrids based on Albasia wood”. Albasia wood is fast-growing, very light and is currently tested according to its technical and environmental capabilities to replace energy-intensive materials such as aluminum.
We showcased our activities in Indonesia with lightwood and the social and environmental aspects of our work with lightwood. To investigate the potential of Albasia wood in innovative applications, we are working together with our partners, the German Aerospace Centre DLR Alfred Kiess GmbH, Volkswagen AG and Broszeit GmbH. The project is funded by BMWK.
We are investigating 3 possible applications of Albasia wood:
- Cars
- Trailers
- Elevators
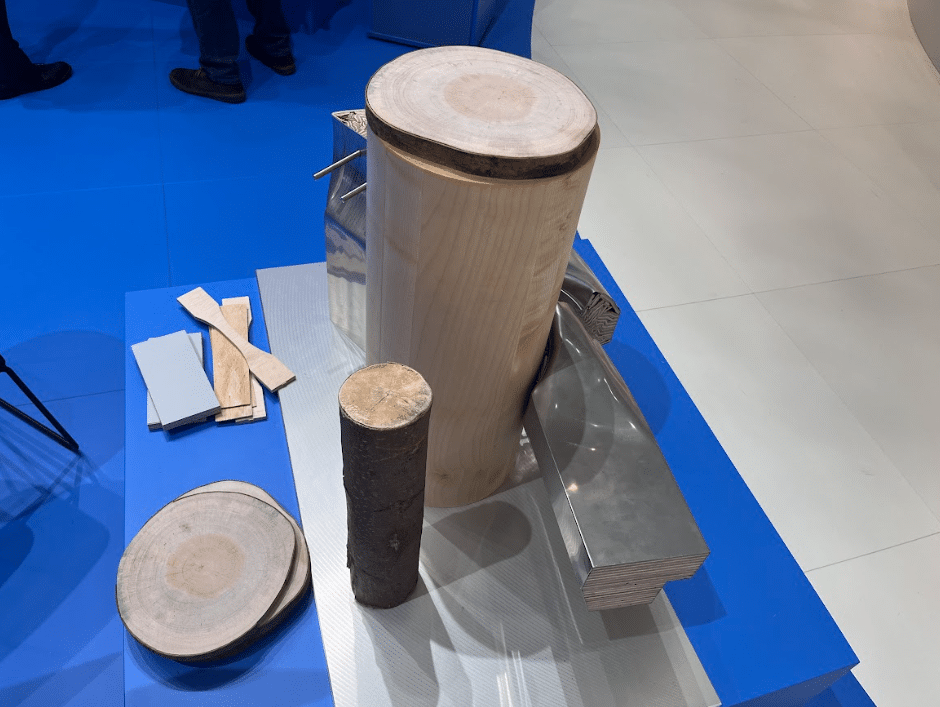
But besides the technical achievements, there are many environmental and social aspects of the „SuMatHrA“ project, equally important as the technical:
Trees play a key role in the mitigation of climate change due to their capability to sequester CO2 from the atmosphere and store it in biomass. Furthermore, wood-based materials are considered not just as renewable resources but also as alternatives to conventional ones (concrete, steel, or plastic) due to their lower environmental impact. Especially in terms of today’s relevant topics – carbon emissions and energy usage.
The „SuMatHra“ project aims to introduce Albasia as a technically reliable material with high climate mitigation potential and broad availability. New applications of the material will create additional demand, which, we hope, will eventually lead to additional incentives to plant trees and higher incomes for tree-planting smallholder farmers.
The goal of our presented „SuMatHra“ project in a nutshell:
- Usage of Albasian‘s wood environmental capabilities to replace energy-intensive materials
such as aluminum and development of sustainable hybrid material systems - CO2 reduction through material substitution
- Reforestation and renaturation of degenerated fallow land, particularly in Indonesia
- Promotion of fair management and sustainable timber value chains